OVERVIEW
Welcome to the Ayurveda Ophthalmology and ENT Department at Sanjeevanam Ayurveda Hospital in Kochi, where we integrate traditional Ayurvedic wisdom with modern medical insights to promote eye, ear, nose, and throat health. Our skilled team of doctors combines Ayurvedic principles with advanced diagnostic tools, authentic therapies, and personalized herbal treatments to offer holistic healthcare solutions. Focused on preventing and treating conditions affecting the eyes, ears, nose, throat, and head, we aim to address the root causes of your health issues. By choosing Sanjeevanam’s Ophthalmology and ENT department, you begin a transformative healing journey that improves your well-being, enhances your quality of life, and helps maintain the health of your sense organs for lasting vitality.

TREATMENTS
At Sanjeevanam, our Ophthalmology and ENT department is committed to offering expertly crafted Ayurvedic treatments for a comprehensive range of conditions affecting the eyes, ears, nose, throat and head. Our specialties include addressing Eye Disorders such as Dry Eyes, Myopia and Diabetic retinopathy along with ENT conditions like Sinusitis, Headaches, Nasal Blockages, Vocal Cord Dysfunction, Hearing Loss, Vertigo and Tinnitus.
Embrace the holistic healing approach of Ayurveda and discover enhanced sensory health and overall well-being at Sanjeevanam.

HIGHLIGHTS
• Eye Health :Comprehensive Ayurvedic care for conditions such as conjunctivitis, dry eyes, myopia, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, macular edema, and other retinal disorders, with personalized treatments for optimal eye health and vision improvement.
• ENT Health :Holistic Ayurvedic treatment for ear conditions like ear discharge, vertigo, tinnitus, otomycosis, Meniere’s disease, hearing loss, and facial palsy. We also provide specialized care for nasal and throat disorders, including allergic rhinitis, vasomotor rhinitis, sinusitis, nasal turbinate hypertrophy, nasal polyps, tonsillitis, and vocal cord cysts.
• Head Ailments :Comprehensive holistic treatments for the effective management of migraines, tension headaches, and related conditions.
• Holistic Health :Expertise in managing eye and ENT conditions affected by lifestyle, environmental, and developmental factors.
• Specialized Care :Our approach incorporates Panchakarma therapies (Ayurvedic detoxification treatments), alongside specialized eye and ENT treatments like Seka (Occular irrigation), Aschyotana (Eye drops), Kavala (Gargling), Karnapoorana (Ear oil retention), and Dhoopana (medicated ear fumigation), to improve overall health and address specific eye and ENT conditions comprehensively.
• Comprehensive Healing Solutions :Integrating Ayurveda, Yoga, Naturopathy, personalized diet and lifestyle guidance to provide preventive, curative, and natural alternatives for long-term eye and ENT health.
• Eye and ENT Care for Lasting Wellness :Focusing on your eye and ENT health, our approach offers a soothing, effective treatment experience for lasting wellness and comfort.
OUR
DOCTORS
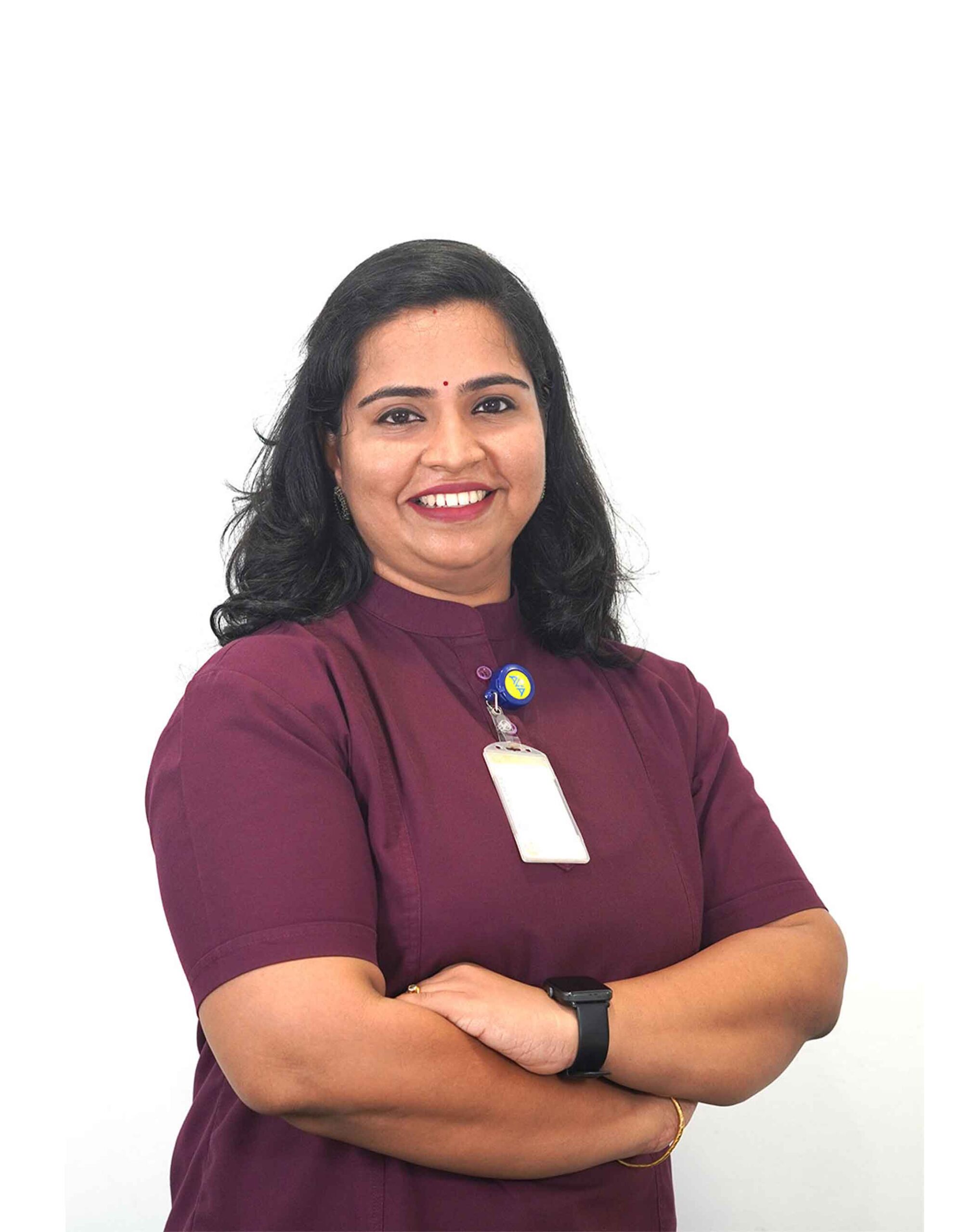

Dr. Neena Ravindran
BAMS, MS (Ay) Senior Medical Officer, Ayurveda Ophthalmology and ENT
Dr. Neena Ravindran is a dedicated and sincere practitioner who holds first rank with Gold medal in her Master’s in Ayurvedic Ophthalmology and ENT. She has conducted evidence-based research on polyherbal ophthalmic formulations in collaboration with IIT MADARAS, which was...
More Info
BOOK APPOINTMENT