Ayurvedic Treatment for Tonsillitis in Kerala
What is Tonsillitis?
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the tonsils, the two lymph nodes located at the back of the throat. This condition can cause a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and other symptoms.
Tonsillitis can be acute, with a sudden onset and short duration, or chronic, with long-term or
recurring symptoms.
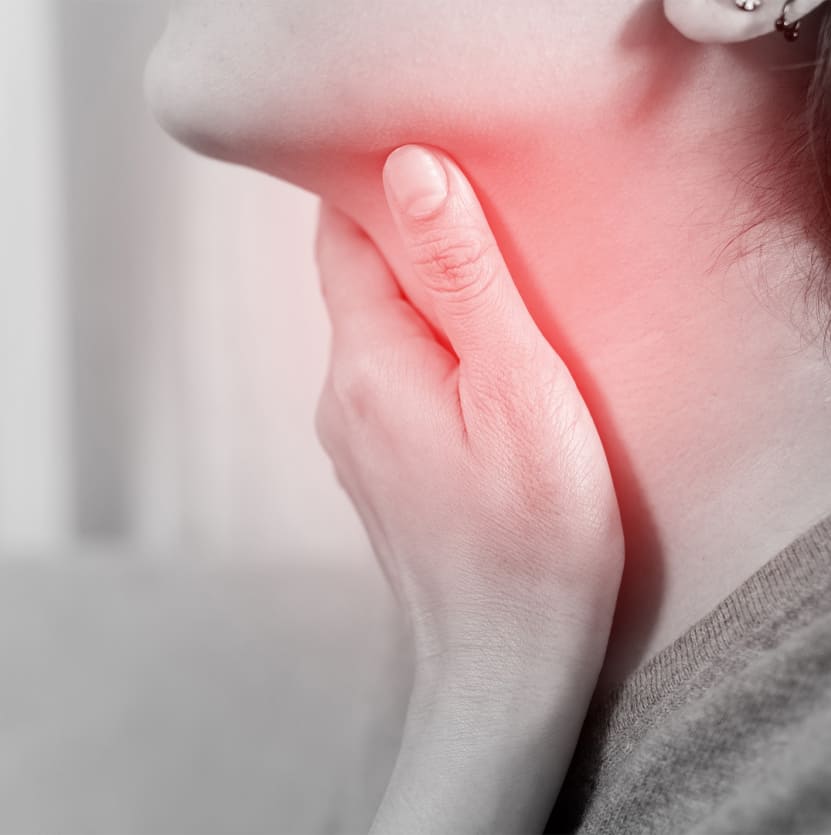
Symptoms
1. Sore Throat: A persistent and often severe sore throat is the most common symptom of tonsillitis.
2. Difficulty Swallowing: Swollen tonsils can make swallowing painful and difficult.
3. Red and Swollen Tonsils: The tonsils may appear red and swollen, sometimes with white or yellow patches or spots.
4. Fever: A high fever is often associated with tonsillitis, especially in cases caused by infection.
5. Enlarged Lymph Nodes: The lymph nodes in the neck may become tender and swollen.
6. Bad Breath: Accumulation of bacteria in the tonsils can cause bad breath.
7. Hoarse Voice: Inflammation can lead to changes in the voice, such as hoarseness.
8. Headache and Ear Pain: Some people experience headaches and ear pain due to the inflammation.

Causes
Tonsillitis is primarily caused by viral or bacterial infections that inflame the tonsils. Common causes include:
1. Viral Infections: Viruses such as the common cold, influenza, or Epstein-Barr virus can cause tonsillitis.
2. Bacterial Infections: Streptococcus bacteria, which cause strep throat, are a common bacterial cause.
3. Environmental Factors: Pollution, smoking, and exposure to allergens can exacerbate tonsillitis.
Types
Acute Tonsillitis:
Duration: Typically lasts a few days to two weeks.
Characteristics: Sudden onset of symptoms, often following a cold or flu.
Chronic Tonsillitis:
Duration: Symptoms persist for an extended period or recur frequently.
Characteristics: Constant or recurrent sore throat, bad breath, and enlarged
tonsils.
Diagnosis
Physical Examination: Checking for swollen tonsils and other signs of infection.
Throat Swab: A sample is taken from the throat to test for bacteria, such as
streptococcus.
Blood Tests: To identify viral infections like mononucleosis.
Treatment
Medications:
Medications: Antibiotics for bacterial infections, pain relievers, and anti-
inflammatory medications to reduce swelling.
Saltwater Gargle:
Gargling with warm salt water can help soothe the throat and reduce swelling.
Rest and Hydration:
Getting plenty of rest and staying hydrated to support the immune system.
Surgery:
Tonsillectomy (removal of tonsils) is considered in severe or recurrent cases
that do not respond to other treatments.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Avoiding irritants such as smoke and maintaining good oral hygiene.
Complications
Peritonsillar Abscess:
A collection of pus around the tonsils that can lead to severe pain and difficulty swallowing.
Chronic Tonsillitis:
Persistent inflammation leading to frequent infections and complications.
Obstructive Sleep Apnea:
Enlarged tonsils can block the airway during sleep, causing breathing difficulties.
Spread of Infection:
Untreated bacterial tonsillitis can lead to infections in other parts of the body, such as the middle ear or sinuses.
Prevention
Good Hygiene:
Regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
Avoid Irritants:
Staying away from smoke, pollutants, and allergens.
Boosting Immunity:
Eating a healthy diet and staying hydrated to support the immune system.
Ayurvedic Management
Ayurveda treats tonsillitis by balancing doshas and reducing inflammation with natural remedies. The dietary approach includes consuming warm, easy-to-digest foods and avoiding cold or spicy foods. Ayurvedic herbs like Tulsi, Licorice, and Turmeric are used to soothe the throat and boost immunity, along with Panchakarma therapies to detoxify the body. Yoga and pranayama exercises are recommended to improve respiratory function and reduce stress.
FREQUENTLY ASKED
QUESTIONS
Q: Can tonsillitis be fully cured?
A: Acute tonsillitis can be cured with appropriate treatment, while chronic tonsillitis may require ongoing management.
Q: Is tonsillitis contagious?
A: Yes, tonsillitis caused by viral or bacterial infections can be contagious.
Q: Can Ayurveda fully cure tonsillitis?
A: Ayurveda offers effective management and can alleviate symptoms, but complete cure depends on the individual’s condition and adherence to treatment.
Q: Is surgery necessary for chronic tonsillitis?
A: Surgery may be recommended for
severe or recurrent cases, but Ayurveda offers non-invasive alternatives that may reduce the need for surgery.
Q: Can diet impact tonsillitis?
A: Yes, following an Ayurvedic diet that avoids cold or spicy foods and incorporates soothing herbs can help manage symptoms.
BOOK APPOINTMENT
























